Graphics
2022.02.09
Both hydraulic pumps and hydraulic motors are energy conversion elements in hydraulic transmission systems. What exactly is the difference between the two? How to differentiate? Where are they applied?
Similarities between hydraulic motors and hydraulic pumps
1. In principle, the hydraulic motor and hydraulic pump are reversible. If driven by a motor, the output is pressure energy (pressure and flow), which is the hydraulic pump; if the pressure oil is input, the output is mechanical energy (torque and flow). speed), it becomes a hydraulic motor.
2. Structurally, the two are similar.

3. The hydraulic motor and the hydraulic pump have the same basic structural elements - a closed and cyclically variable volume and a corresponding oil distribution mechanism. The working principle of hydraulic motor and hydraulic pump is to use the change of sealing working volume to absorb and discharge oil.
For hydraulic pumps, oil is sucked when the working volume increases, and high-pressure oil is discharged when the working volume decreases. For hydraulic motors, high-pressure oil enters when the working volume increases, and low-pressure oil is discharged when the working volume decreases.
Differences between hydraulic motors and hydraulic pumps
1. The hydraulic pump is a conversion device that converts the mechanical energy of the motor into hydraulic energy. It outputs flow and pressure, and it is hoped that the volumetric efficiency is high; the hydraulic motor is a conversion device that converts the pressure energy of the liquid into mechanical energy, and outputs torque and rotational speed. efficient. Therefore, the hydraulic pump is the energy device, and the hydraulic motor is the actuator.
2. The steering of the output shaft of the hydraulic motor must be able to rotate forward and reverse, so its structure is symmetrical; while some hydraulic pumps (such as gear pumps, vane pumps, etc.) have clear regulations on the steering, which can only be rotated in one direction, not at will. Change the selection direction.
3. In addition to the oil inlet and outlet ports, the hydraulic motor also has a separate oil leakage port; the hydraulic pump generally only has the oil inlet and oil outlet ports (except for the axial piston pump), and the leakage oil in it is communicated with the oil inlet port.
4. The volumetric efficiency of hydraulic motors is lower than that of hydraulic pumps.
5. Usually the working speed of the hydraulic pump is relatively high, while the output speed of the hydraulic motor is low.
6. In addition, the oil suction port of the gear pump is large and the oil discharge port is small, while the suction port and the oil discharge port of the gear hydraulic motor are the same size.
7. The gear motor has more teeth than the gear pump.
8. The vane of the vane pump must be installed obliquely, while the vane of the vane motor is installed radially; the vane of the vane motor relies on the swallow-type spring at the root to be pressed against the surface of the stator, while the vane of the vane pump relies on the pressure of the root. Oil and centrifugal force act on the stator surface.
In terms of working principle, both hydraulic motors and hydraulic pumps work by changing the volume of the sealed working chamber. However, due to their different use purposes, there are many differences in structure, and generally they cannot be directly reversed.
Classification of hydraulic pumps
According to the structure, it is divided into three categories: plunger pump, gear pump and vane pump.
According to whether the displacement is adjustable: quantitative pump, variable pump.
According to the direction of oil discharge: one-way pump, two-way pump.
According to the pressure level: low pressure, medium pressure, medium high pressure, ultra-high pressure pump.
Gear pump: small in volume, simple in structure, less strict on oil cleanliness, and cheaper in price; but the pump shaft is subject to unbalanced force, serious wear, and large leakage.
Gear pumps are widely used in mining equipment, metallurgical equipment, construction machinery, construction machinery, agricultural and forestry machinery and other industries.

Vane pump: divided into double-acting vane pump and single-acting vane pump. This kind of pump has uniform flow, stable operation, low noise, higher working pressure and volumetric efficiency than gear pump, and more complicated structure than gear pump. High-pressure vane pumps are used in the hydraulic systems of lifting and transport vehicles and construction machinery.
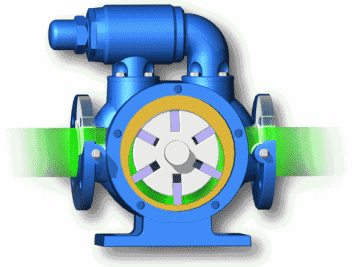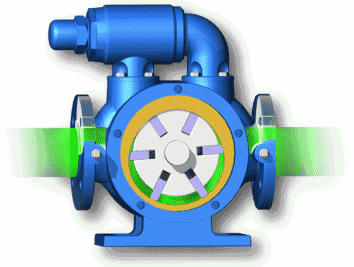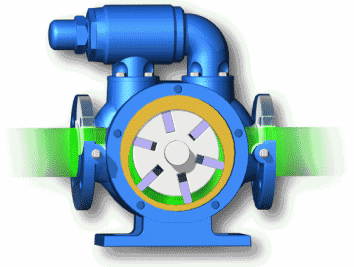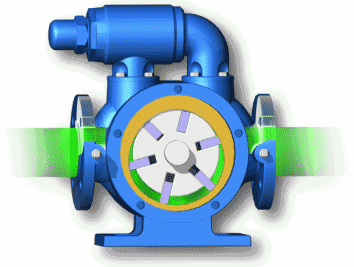
Plunger pump: high volumetric efficiency, small leakage, can work under high pressure, mostly used in high-power hydraulic systems; but complex structure, high requirements for materials and processing accuracy, high price, and high requirements for oil cleanliness. Plunger pumps are often used in cycling diesel engines to deliver high-pressure fuel.

Classification of hydraulic motors
According to the structure, it is divided into several main forms: gear type, vane type and plunger type.
According to the speed and torque range: high-speed motor and low-speed motor.
The gear type hydraulic motor is simple in structure and cheap in price, and is often used in occasions where high speed, low torque and low requirements for motion stability are not required. Such as driving grinders, fans, etc.
The vane hydraulic motor has small rotational inertia, sensitive action, low volumetric efficiency, and soft mechanical characteristics.
The axial piston motor has high volumetric efficiency, large adjustment range, and good low-speed stability.
Previous:Tolerance Rules in Non-Standard Mechanical Drawings
Next:Nine major errors in machining, how many do you know?
Related Information
- Industry news
- The tap or drill bit breaks in the hole, how to fix it?
- Why do airplanes use rivets instead of welding?
- Why are engineering drawings all blueprints?
- How is a ping pong ball made? It turns out that it is made of two pieces of plas
- What to do if quality is abnormal? Doing these 3 things well is the key!
- Weekly News 9.7-9.13
- Huawei's three-fold screen is approaching, and the domestic supply chain is wait
- Innovative application of digital twin technology in integrated die-casting prod
- 5 types of carbide cutting tools, what are the differences? Save this article an
- Global manufacturing PMI in June was 49.5% | Weekly News 7.6-7.12
- Raw material defects | Machining special operations and practical cases 109
- No wonder Toyota stamping is so good: a day in the life of a Toyota stamping sho
- Analysis on the development trend and demand of China's mold industry
- How many types of sealing rings are there in machinery? What are they used for?
- Hangfa, Hangfa, a scar on the hearts of machine processing workers
- How to mill a large arc surface with a small cutter?
- Dynamics of the processing center of the process! What is the fundamental reason
- 500 ° C ultra -strong aluminum alloy! This problem is overcome
- How much do you know about the hometown of machine tools and molds, how much do

 BACK
BACK MT HOME
MT HOME Navbar
Navbar