How to tighten flange bolts is scientifically standardized? do you know?
2021.07.19
1.Inspection of flange fasteners
● Gasket: When installing, make sure that the gasket is new, clean and dry, and check whether the gasket is defective or damaged; the old gasket cannot be reused; before installation, confirm the size and grade of the gasket used and the flange The logos are the same.
● Flange: Before installation, check whether the flange surface is damaged, such as scratches, nicks, mud, corrosion and burrs, and the dents that penetrate the water line of the flange sealing surface radially, and the depth of the scratch exceeds 0.2mm, and When the coverage area exceeds half the width of the gasket sealing surface, the flange must be replaced or the sealing surface reprocessed and repaired; the nut supporting surface on the back of the flange should be parallel and smooth; check whether the flange is aligned, and the inspection method should be in accordance with SH3501-2011 6.2 Pipeline installation requirements.
● Bolts and nuts: Check whether the bolts and nuts are used correctly according to the equipment and pipeline design requirements; the threads and contact surfaces must not have dirt, rust, heavy skin, nicks, burrs, chips and other foreign substances that affect the torque during the tightening process ; It is not allowed to repair the bolts by welding or machining methods; after the flange is installed and tightened, at least two threads are exposed outside the nut; the bolts and nuts must be lubricated before use, so that the bolts have low friction when tightening Coefficient and improve the anti-slippage and corrosion resistance of bolts and nuts; stud threads, nut threads and contact surfaces must be degreased and dried before using lubricating oil; on bolt threads, nut threads, nut bearing surfaces, washers, and flanges The supporting surface of the nut should properly use uniform lubricating oil; use high temperature anti-seize agent as needed.
2.Bolt fastening method
● Non-torque torx wrench or hammer wrench: suitable for general equipment and pipe flange fastening. It is selected according to bolt size and flange pressure rating. The tightening requirements are as follows:
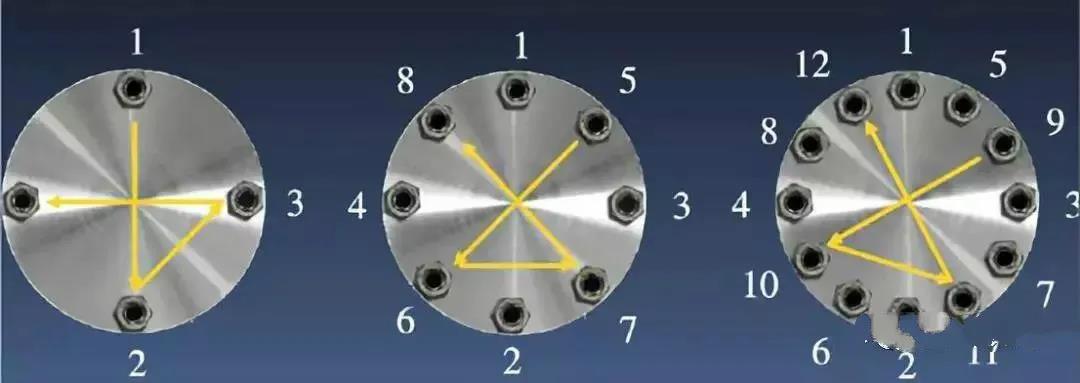
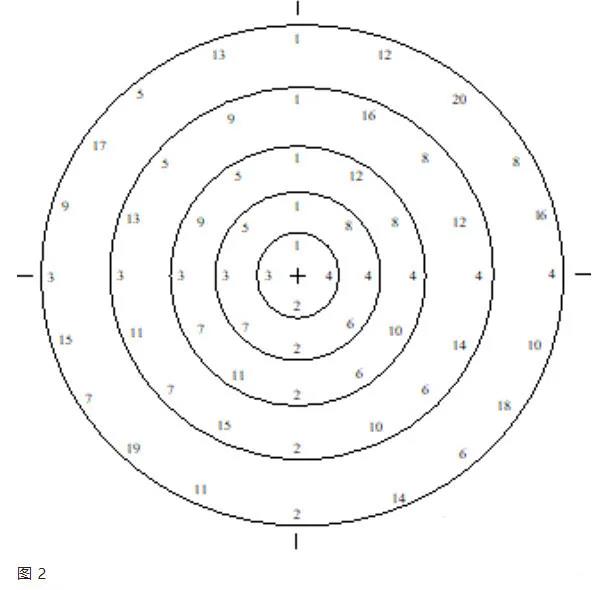
1) The maintenance unit shall formulate a tightening plan, symmetrically tighten the flanges, and number the tightening sequence. Refer to Figure 1 and Figure 2 for numbering.
2) Use 4 bolts to locate the gasket at positions 1, 2, 3, 4, and ensure that the center of the wound gasket is within the flange edge.
3) Tighten the positioning bolts by hand, and then insert other stud bolts and tighten them to balance the load. Make sure that at least 2 threads are exposed at each end of the nut.
4) According to the field equipment and flanges, a tightening circle is calculated once, and the number of tightening (at least 3 times) and the percussion load (strength) of each tightening are determined reasonably. The tightening percussion load (strength) is Tighten in order from small to large (such as 50%, 80%, 100% increments). Do not load the load too fast or too large to prevent the gasket seal from failing.
5) The sequence of each tightening of a torqueless box wrench or hammer wrench: tighten the two diametrically opposed bolts to the bolt's predetermined hammering load (strength); tighten the two bolts about 90 degrees apart from the previous two bolts along the circumference Another pair of bolts; continue tightening until all other bolts are tightened to the intended hammer load.
6) Finally, tighten all bolts in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction with 100% hammering load (strength).
● Torque wrench: suitable for important equipment and pipeline flanges such as high temperature and high pressure, inflammable and explosive. The tightening requirements are as follows:
1) The maintenance unit needs to formulate a tightening plan, formulate a suitable torque, and conduct a design review according to the bolt strength, the initial seal specific pressure of the gasket, the working seal specific pressure, and the medium pressure to prevent bolt fracture and gasket compression. Excessive force and loss of elasticity lead to seal failure.
2) Fasten the flanges symmetrically, and number the tightening sequence. Refer to Figure 1 and Figure 2 for the number.
3) Use 4 bolts to locate the gasket at positions 1, 2, 3, 4, and ensure that the center of the wound gasket is within the flange edge.
4)Tighten the positioning bolts by hand, and then insert other stud bolts and tighten them to balance the load. Make sure that at least 2 threads are exposed at each end of the nut.
5) According to the field equipment and flanges, a tightening circle is calculated once, and the number of tightening (at least 3 times) and each tightening torque are reasonably set. The tightening torque is tightened in order from small to large (such as 50%, 80%, 100% increment), the load cannot be loaded too fast or too large to prevent the gasket seal from failing.
6) The sequence of each tightening of the torque wrench: tighten the two diametrically opposed bolts to the bolt's predetermined torque; tighten another pair of bolts about 90 degrees apart from the previous two bolts along the circumference; continue tightening until all other bolts The bolts are all tightened to a predetermined torque.
7) Finally, tighten all bolts in a clockwise or counterclockwise direction at 100% torque.
8) Record the torque value for reference for future maintenance.
● Bolt tensioner: suitable for important equipment and pipeline flanges such as high temperature and high pressure, inflammable and explosive. The tightening requirements are as follows:
1) The maintenance unit formulates a tightening plan, formulates a suitable tensile force, and conducts a design review based on the bolt strength, the initial seal specific pressure of the gasket, the working seal specific pressure, and the medium pressure to prevent bolt fracture and gasket pressure. Excessive tightening force and loss of elasticity lead to seal failure.
2) When the bolt tensioner stretches the tightened bolts individually (step by step), according to the principle of uniformity of bolt tightening, refer to the tightening sequence of the torque wrench for tightening.
3) During the tension and tightening process of the bolt tensioner, set the number of tension and tightening reasonably, and pressurize from small to large (such as 50%, 80%, 100%), uniformly pressurize, and every time a certain pressure is increased, Increase the voltage after stabilization to avoid excessive impact tension and affect the pre-tightening effect of the bolt.
4) Record the pressure value for reference for future maintenance.
2. Thermal tightness requirements for equipment and pipeline heating during the start of construction
(1) Perform hot tightening according to the temperature in Table 1
Table 1 Hot and cold fastening temperature of equipment and pipes unit: ℃
Working temperature Primary heat tight and cold tight temperature Second hot tight and cold tight temperature
250~350 working temperature -
>350 350 working temperature
-70~-29 Working temperature -
<-70 -70 working temperature
Note: If the working temperature is between -29°C and 250°C, heat tightening and cold tightening are not required.
(2) Hot or cold tightening should be carried out after the temperature of the equipment and pipeline is stable. Use explosion-proof tools. During the tightening, no heating or pressure boosting operations are allowed.
(3) When tightening, it is recommended to start from the largest flange gap and tighten symmetrically. If there is a leak, perform a tight leak first.
(4) During the heating process of equipment and pipelines during the start of construction, tightening quality inspection is required. Use a torque wrench to press 100% torque value or use an explosion-proof hammer tool to hammer the nut in the tightening direction to check whether it is loose.
Previous:Basic knowledge of rolling bearing
Next:Why is the tool intentionally passivated? Ten years of teachers do not necessarily understand!
Related Information
- Industry news
- The tap or drill bit breaks in the hole, how to fix it?
- Why do airplanes use rivets instead of welding?
- Why are engineering drawings all blueprints?
- How is a ping pong ball made? It turns out that it is made of two pieces of plas
- What to do if quality is abnormal? Doing these 3 things well is the key!
- Weekly News 9.7-9.13
- Huawei's three-fold screen is approaching, and the domestic supply chain is wait
- Innovative application of digital twin technology in integrated die-casting prod
- 5 types of carbide cutting tools, what are the differences? Save this article an
- Global manufacturing PMI in June was 49.5% | Weekly News 7.6-7.12
- Raw material defects | Machining special operations and practical cases 109
- No wonder Toyota stamping is so good: a day in the life of a Toyota stamping sho
- Analysis on the development trend and demand of China's mold industry
- How many types of sealing rings are there in machinery? What are they used for?
- Hangfa, Hangfa, a scar on the hearts of machine processing workers
- How to mill a large arc surface with a small cutter?
- Dynamics of the processing center of the process! What is the fundamental reason
- 500 ° C ultra -strong aluminum alloy! This problem is overcome
- How much do you know about the hometown of machine tools and molds, how much do

 BACK
BACK MT HOME
MT HOME Navbar
Navbar