Preparation and heat treatment of pre -welding and after welding heat treatment
2023.05.11
Pre -welding
Preparatory preheating and after welding heat treatment is very important for ensuring welding quality. The welding of important components, the welding of alloy steel, and the welding of thick components require preheating before welding. The main role of preheating preheating before welding is as follows:
(1) The preheating can slow down the cooling speed after welding, which is conducive to the proliferation of hydrogen in the metal of the weld metal, and avoiding a hydrogen crack. At the same time, it also reduces the hardening of welds and thermal influence areas, and improves the cracking resistance of the welding joint.
(2) Preheating can reduce welding stress. Uniform local preheating or overall preheating can reduce the temperature difference between welded parts (also known as temperature gradient). In this way, the welding stress is reduced on the one hand, and on the other hand, the welding rate is reduced, which is conducive to avoiding welding cracks.
(3) Preheating can reduce the restraint of the welding structure, and the restraint of reducing angle connector is particularly obvious. As the preheating temperature increases, the incidence of cracks decreases.
The choice of preheating temperature and inter -layer temperature is not only related to the chemical composition of steel and stunts, but also related to the rigidity, welding method, and ambient temperature of the welding structure. These factors should be considered comprehensively. In addition, the uniformity of the preheating temperature in the thick direction of the steel plate and the uniformity in the weld area have an important impact on reducing the welding stress. The width of the local warm-up should be dependent on the restraint of the welded carrier. Generally, it should be three times the wall thickness around the weld area, and it should not be less than 150-200 mm. If the preheating is uneven, not only does not reduce the welding stress, but it will increase the welding stress.
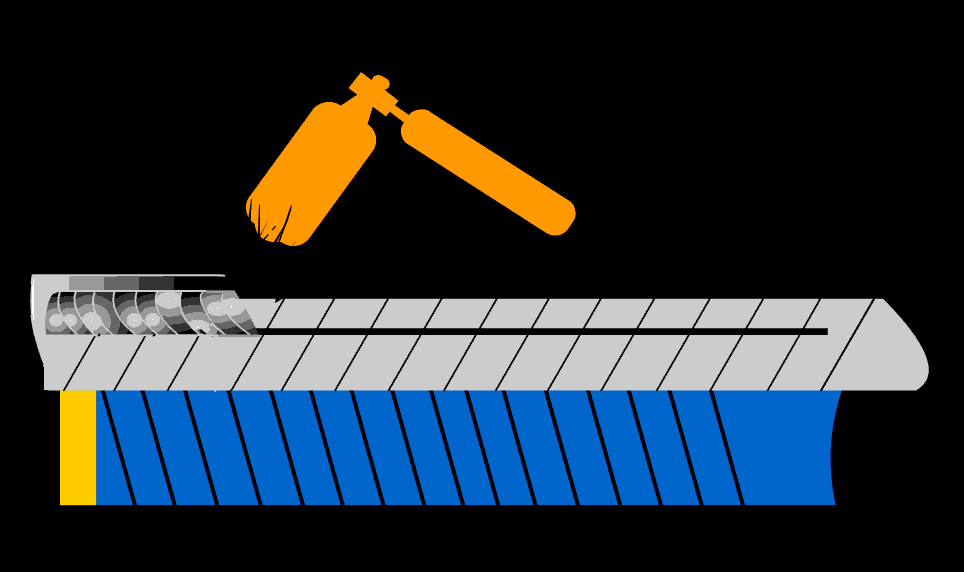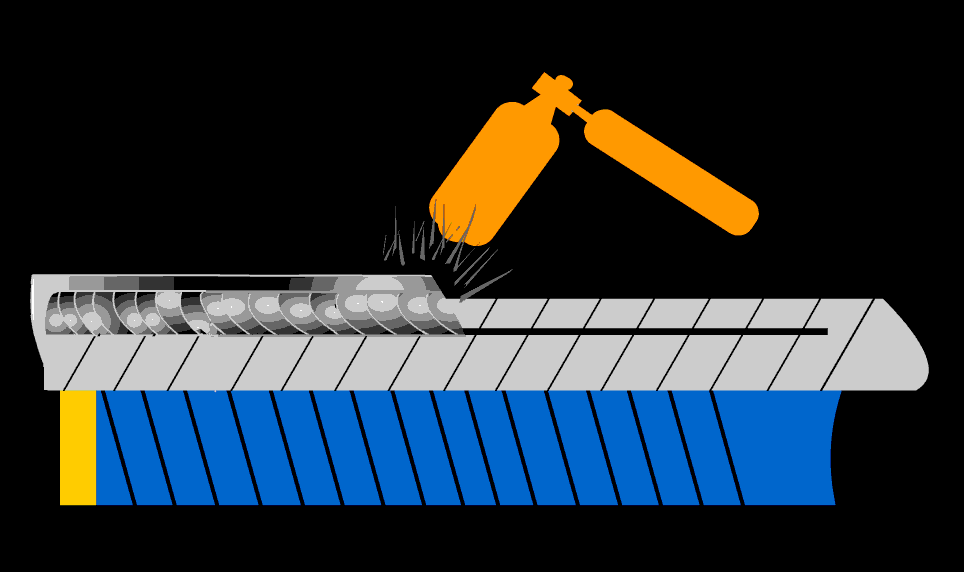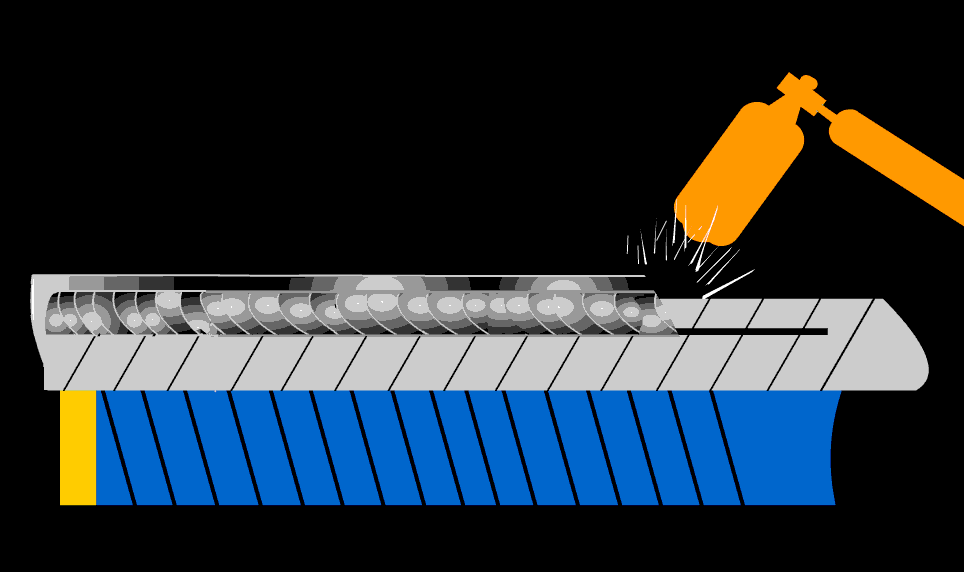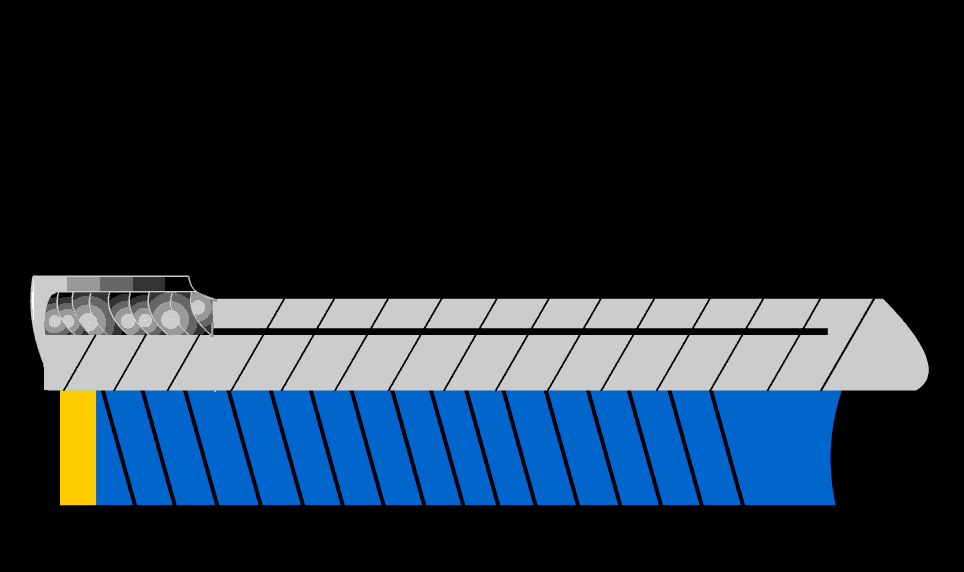
After welding heat treatment
There are three goals of the heat treatment after welding: hydrogen eliminating, eliminating welding stress, improving weld tissue and comprehensive performance.
After welding, the hydrogenation treatment refers to the low temperature heat treatment performed when the weld has not been cooled to less than 100 ° C after the welding is completed. The general specifications are heated to 200 ~ 350 ° C, and heat preservation for 2-6 hours. The main role of hydrogen per after welding is to speed up the recovery of hydrogen in the weld and thermal influence area, which is extremely significant for preventing the welding cracks from welding and cracking during welding of low alloy steel.
During the welding process, due to the unevenness of heating and cooling, as well as restraint or plus restraint of the component itself, welding stress will always be generated in the component after the welding work is over. The existence of welding stress in the component will reduce the actual carrying capacity of the welding joint area, produce plastic deformation, and in severe cases, it will also cause the component to damage.
Ethical stress thermal treatment is to make the welding workpiece decreased at high temperature state to achieve the purpose of relaxing welding stress. There are two commonly used methods: one is to ignite the overall high temperature, that is, put the overall welding parts into the heating furnace, slowly heated to a certain temperature, and then heat the heat for a while, and finally cool down in the air or in the furnace. This method can eliminate 80%-90%welding stress. Another method is the local high temperature recovery, that is, only heating the welds and its nearby areas, and then slowly cooled, reducing the peak of welding stress, making the stress distribution relatively smooth, and partially to partially eliminate welding stress.
After welding, some alloy steel materials will have a harder tissue, which will deteriorate the mechanical properties of the material. In addition, this harder tissue may lead to damage to the joint under the action of welding stress and hydrogen. If the heating treatment is improved, the gold phase tissue of the joints improves, which improves the plasticity and toughness of the welding joint, thereby improving the comprehensive mechanical properties of the welding joint.
Previous:What are the differences in different thermal treatment processes?
Next:The most commonly used metal material for mechanical design
Related Information
- Industry news
- The tap or drill bit breaks in the hole, how to fix it?
- Why do airplanes use rivets instead of welding?
- Why are engineering drawings all blueprints?
- How is a ping pong ball made? It turns out that it is made of two pieces of plas
- What to do if quality is abnormal? Doing these 3 things well is the key!
- Weekly News 9.7-9.13
- Huawei's three-fold screen is approaching, and the domestic supply chain is wait
- Innovative application of digital twin technology in integrated die-casting prod
- 5 types of carbide cutting tools, what are the differences? Save this article an
- Global manufacturing PMI in June was 49.5% | Weekly News 7.6-7.12
- Raw material defects | Machining special operations and practical cases 109
- No wonder Toyota stamping is so good: a day in the life of a Toyota stamping sho
- Analysis on the development trend and demand of China's mold industry
- How many types of sealing rings are there in machinery? What are they used for?
- Hangfa, Hangfa, a scar on the hearts of machine processing workers
- How to mill a large arc surface with a small cutter?
- Dynamics of the processing center of the process! What is the fundamental reason
- 500 ° C ultra -strong aluminum alloy! This problem is overcome
- How much do you know about the hometown of machine tools and molds, how much do

 BACK
BACK MT HOME
MT HOME Navbar
Navbar