What models are available in stainless steel?
2022.03.04
The sulfur content of steel shall not exceed 0.05%; the phosphorus content in general steel is limited to less than 0.0%.
Therefore, the content of sulfur and phosphorus is a very important indicator, and carbon structural steel and high-quality carbon structural steel are divided according to it:
Steel with sulfur and phosphorus content not exceeding 0.04% is called high-quality steel;
Steel with a sulfur content of not more than 0.03% and a phosphorus content of not more than 0.035% is called high-quality steel;
The steel with sulfur and phosphorus content not exceeding 0.025% is called super quality steel.
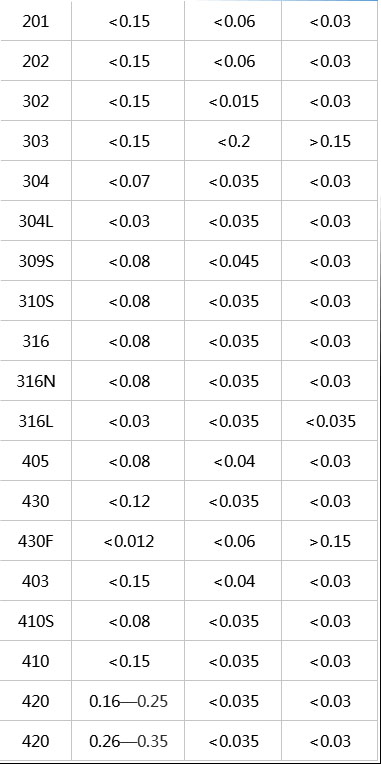
Common stainless steel sulfur and phosphorus content
Grade Carbon content Phosphorus content Sulfur content
2. Common stainless steel models
Commonly used stainless steel models are often represented by digital symbols, including 200 series, 300 series, and 400 series, which are the representation methods in the United States, such as 201, 202, 302, 303, 304, 316, 410, 420, 430, etc. The stainless steel model in China is It is represented by element symbols and numbers, such as 1Cr18Ni9, 0Cr18Ni9, 00Cr18Ni9, 1Cr17, 3Cr13, 1Cr17Mn6Ni5N, etc. The numbers represent the corresponding element content.
200 Series: Chromium-Nickel-Manganese Austenitic Stainless Steels
300 Series: Chromium-Nickel Austenitic Stainless Steels
301: Good ductility, used for molded products. It can also be hardened by machine speed. Good weldability. Wear resistance and fatigue strength are better than 304 stainless steel.
302: The corrosion resistance is the same as that of 304, and the strength is better due to the relatively high carbon content.
302B: It is a kind of stainless steel with high silicon content, which has high resistance to high temperature oxidation.
303: By adding a small amount of sulfur and phosphorus to make it more machining.
303Se: Also used to make parts that require hot upsetting, because under these conditions, this stainless steel has good hot workability.
304: ie 18/8 stainless steel. GB grade is 0Cr18Ni9. 309: Compared with 304, it has better temperature resistance.
304L: A variant of 304 stainless steel with a lower carbon content, used where welding is required. The lower carbon content minimizes carbide precipitation in the heat-affected zone near the weld, which can lead to intergranular corrosion (weld erosion) of stainless steel in some environments.
304N: It is a nitrogen-containing stainless steel. Nitrogen is added to improve the strength of the steel.
305 and 384: high nickel content, low work hardening rate, suitable for various occasions requiring high cold formability.
308: Used to make welding rods.
309, 310, 314 and 330: nickel and chromium content are relatively high, in order to improve the oxidation resistance and creep strength of steel at high temperature. 30S5 and 310S are variants of 309 and 310 stainless steel, the only difference being that the carbon content is lower, in order to minimize the precipitation of carbides near the weld. 330 stainless steel has a particularly high resistance to carburization and thermal shock resistance.
316 and 317: contain aluminum, so the resistance to pitting corrosion in marine and chemical industry environments is much better than 304 stainless steel. Among them, 316 stainless steel variants include low carbon stainless steel 316L, nitrogen-containing high-strength stainless steel 316N, and free-cutting stainless steel 316F with high sulfur content.
321, 347 and 348: stainless steel stabilized with titanium, niobium plus tantalum and niobium respectively, suitable for welding components used at high temperatures. 348 is a kind of stainless steel suitable for the nuclear power industry, which has certain restrictions on the combined amount of tantalum and diamond.
400 Series: Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steels
408: good heat resistance, weak corrosion resistance, 11% Cr, 8% Ni
409: The cheapest model (UK and US), usually used as a car exhaust pipe, is a ferritic stainless steel (chrome steel)
410: Martensitic (high-strength chromium steel), with good wear resistance and poor corrosion resistance. 416: The addition of sulfur improves the processing properties of the material.
420: "Cutting-grade" martensitic steel, the earliest stainless steel similar to Brinell's high-chromium steel. Also used in surgical knives, can do very bright
430: Ferritic stainless steel, decorative, eg for car accessories. Good formability, but poor temperature and corrosion resistance
440: High-strength cutting tool steel with slightly higher carbon content. After proper heat treatment, higher yield strength can be obtained, and the hardness can reach 58HRC, which is one of the hardest stainless steels. The most common application example is "razor blades". There are three commonly used models: 440A, 440B, 440C, and 440F (easy to process)
500 Series: Heat Resistant Chromium Alloy Steel
600 Series: Martensitic Precipitation Hardening Stainless Steels
630: The most commonly used type of precipitation hardening stainless steel, usually also called 17-4; 17%Cr, 4%Ni
Previous:Bearings want to be assembled, these basics must be kept in mind
Next:How to do non-standard mechanical design, old mechanical engineers tell you!
Related Information
- Industry news
- The tap or drill bit breaks in the hole, how to fix it?
- Why do airplanes use rivets instead of welding?
- Why are engineering drawings all blueprints?
- How is a ping pong ball made? It turns out that it is made of two pieces of plas
- What to do if quality is abnormal? Doing these 3 things well is the key!
- Weekly News 9.7-9.13
- Huawei's three-fold screen is approaching, and the domestic supply chain is wait
- Innovative application of digital twin technology in integrated die-casting prod
- 5 types of carbide cutting tools, what are the differences? Save this article an
- Global manufacturing PMI in June was 49.5% | Weekly News 7.6-7.12
- Raw material defects | Machining special operations and practical cases 109
- No wonder Toyota stamping is so good: a day in the life of a Toyota stamping sho
- Analysis on the development trend and demand of China's mold industry
- How many types of sealing rings are there in machinery? What are they used for?
- Hangfa, Hangfa, a scar on the hearts of machine processing workers
- How to mill a large arc surface with a small cutter?
- Dynamics of the processing center of the process! What is the fundamental reason
- 500 ° C ultra -strong aluminum alloy! This problem is overcome
- How much do you know about the hometown of machine tools and molds, how much do

 BACK
BACK MT HOME
MT HOME Navbar
Navbar