The CNC tool is named like this, so you can see it at a glance!
2021.03.17
Category group 1 xxyyy (milling cutter):
110 Spherical milling cutter (cylindrical milling cutter, the letter y after it represents the diameter of the milling cutter, the following is abbreviated)
120 end mill
140 face milling cutter
150 disc cutter
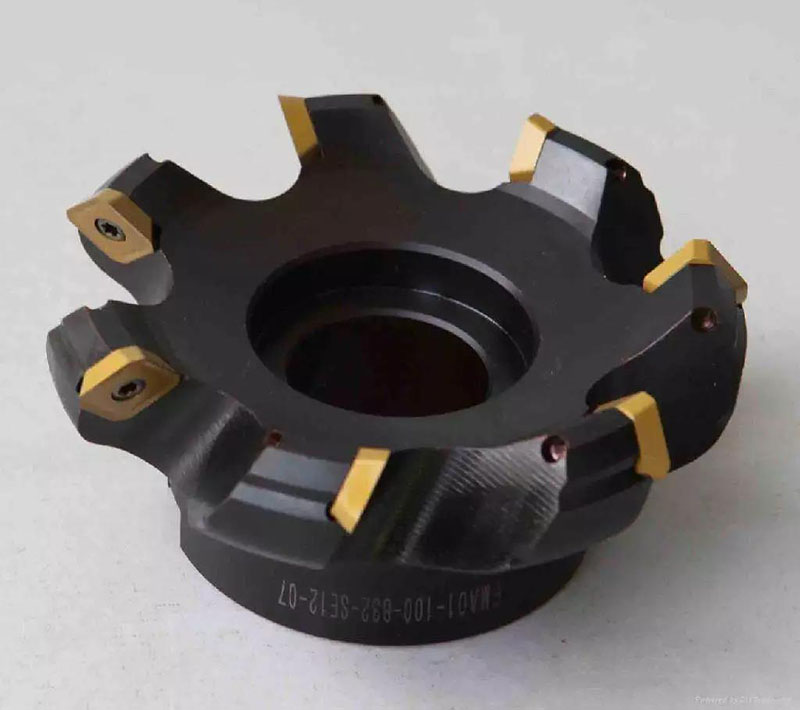

Category group 2 xxyyy (drills)
200 twist drill (the letter y after it stands for the diameter of the drill bit, the following is a little bit the same)
220 center drill
240 normal thread tap (the letter y after that can distinguish coarse thread or fine thread)
250 reamer

Category group 3 xxyyy (boring tool)
300 double-edged rough boring tool (the letter y after it represents the diameter of the boring tool, the following is a little bit the same)
320 single-edged precision boring cutter

Category group 4 xxyyy (reaming knife)
400 reaming knife (the letter y after that stands for the diameter of the reaming knife, the following is a bit the same)

Category group 5 xxyyy (turning tool):
500 rough turning tool (the letter y after that represents the value of the arc of the tool tip, the following is abbreviated)
510 Fine Turning Tool
520 grooving knife (the letter y after it stands for the width of the knife tip, the following is a little bit the same)
530 Cutting tool
540 thread turning tool (the letter y after that can represent parameters such as coarse or fine thread)
Category group 7 xxyyy (special tool, the meaning of the letter y thereafter depends on the specific situation)
Examples are as follows:
T110010 represents a spherical milling cutter with a diameter of 10 mm;
T200020 represents a twist drill with a diameter of 20 mm;
T300100 represents a double-edged rough boring tool with a diameter of 100 mm;
T400110 represents a hole reaming knife with a diameter of 110 mm;
T500008 represents a rough turning tool with a tip arc of R0.8 mm;
in conclusion
In this numbering method, the tool number itself contains many contents such as tool type, specific model and size, so that programmers and operators can understand the use of each tool at a glance, especially when the machine tool program is not Chinese. A unified numbering method can not only have a more intuitive understanding of the CNC machining process, and avoid quality accidents caused by incorrect use of tools; greatly reduce processing preparation time and improve production efficiency; at the same time, the company's tool management work can be more standardized and Scientific, improve the automation level of tool management, achieve the purpose of quick query and effective use of tool resources, and is suitable for all kinds of CNC machine tools.
Nevertheless, due to the different types of CNC machine tools and tools in each unit, the above methods are still insufficient; here is only a personal idea, hoping to play a role in attracting ideas, and experts are invited to criticize and correct us for any improprieties. .
Factors affecting the selection of CNC tools

When choosing the type and specification of the tool, the following factors are mainly considered:
(1) Nature of production
The nature of production here refers to the batch size of the parts, which mainly considers the impact on tool selection from the processing cost.
For example, it may be cost-effective to use special tools in mass production, while in single or small batch production, it is more suitable to choose standard tools.
(2) Type of machine tool
The influence of the CNC machine tool used to complete the process on the selected tool type (drill, turning tool or milling tool). Under the condition that the rigidity of the workpiece system and the tool system can be guaranteed, high-productivity tools, such as high-speed cutting tools and large-feed tools, are allowed.
(3) CNC machining plan
Different CNC machining programs can use different types of tools. For example, drilling and reaming can be used for hole processing, or drilling and boring tools can be used for processing.
(4) The size and shape of the workpiece
The size and shape of the workpiece also affect the selection of tool types and specifications. For example, special tools must be used to process special-shaped surfaces.
(5) Machining surface roughness
The surface roughness of the machined affects the structure shape and cutting amount of the tool. For example, rough milling cutters can be used for rough milling of blanks, and fine-tooth milling cutters are best used for finishing milling.
(6) Machining accuracy
The machining accuracy affects the type and structure of the finishing tool. For example, the final machining of the hole can be processed with a drill, a reaming drill, a reamer or a boring tool according to the accuracy of the hole.
(7) Workpiece material
The workpiece material will determine the choice of tool material and geometric parameters of the cutting part. The tool material is related to the machining accuracy and material hardness of the workpiece.
Performance requirements of CNC tools
Because CNC machine tools have the characteristics of high processing accuracy, high processing efficiency, concentrated processing procedures and few parts clamping times, higher requirements are put forward for the CNC tools used. In terms of tool performance, CNC tools should be higher than those used by ordinary machine tools.
When choosing a CNC tool, the standard tool should be selected first, and a variety of high-efficiency composite tools and special special tools can be selected when necessary. When choosing standard CNC tools, you should choose various advanced tools as much as possible based on the actual situation, such as indexable tools, solid carbide tools, ceramic tools, etc.
When choosing CNC machine tools for processing tools, the following issues should also be considered:
(1) The type, specification and accuracy grade of the CNC tool should be able to meet the processing requirements, and the tool material should be compatible with the workpiece material.
(2) Good cutting performance. In order to adapt to the tool's ability to use a large backfeed and high feed rate when roughing or processing difficult-to-machine materials, the tool should have the ability to withstand high-speed cutting and powerful cutting. At the same time, the same batch of tools must be stable in terms of cutting performance and tool life, in order to realize tool change according to tool life or the CNC system to manage the tool life.
(3) High precision. In order to meet the requirements of high precision and automatic tool change of CNC machining, the cutting tools must have high accuracy. For example, the radial dimension accuracy of some integral end mills is as high as 0.005mm.
(4) High reliability. To ensure that there will be no accidental damage and potential defects of the tool in the CNC machining, which will affect the smooth progress of the machining, the tool and the accessories combined with it must have good reliability and strong adaptability.
(5) High durability. CNC machining tools, whether in roughing or finishing, should have higher durability than those used in ordinary machine tools, so as to minimize the number of times of changing or grinding tools and tool setting, thereby improving the processing efficiency of CNC machine tools And to ensure the quality of processing.
(6) Good chip breaking and chip removal performance. In CNC machining, chip breaking and chip removal are not handled manually like ordinary machine tools. Chips are easy to wrap around the tool and workpiece, which will damage the tool and scratch the machined surface of the workpiece, and even cause injury and equipment accidents. Affect the processing quality and the safe operation of the machine tool, so the tool is required to have better chip breaking and chip removal performance.
Previous:Why preheat the machine tool?
Next:Classification of surface roughness of parts!
Related Information
- Industry news
- The tap or drill bit breaks in the hole, how to fix it?
- Why do airplanes use rivets instead of welding?
- Why are engineering drawings all blueprints?
- How is a ping pong ball made? It turns out that it is made of two pieces of plas
- What to do if quality is abnormal? Doing these 3 things well is the key!
- Weekly News 9.7-9.13
- Huawei's three-fold screen is approaching, and the domestic supply chain is wait
- Innovative application of digital twin technology in integrated die-casting prod
- 5 types of carbide cutting tools, what are the differences? Save this article an
- Global manufacturing PMI in June was 49.5% | Weekly News 7.6-7.12
- Raw material defects | Machining special operations and practical cases 109
- No wonder Toyota stamping is so good: a day in the life of a Toyota stamping sho
- Analysis on the development trend and demand of China's mold industry
- How many types of sealing rings are there in machinery? What are they used for?
- Hangfa, Hangfa, a scar on the hearts of machine processing workers
- How to mill a large arc surface with a small cutter?
- Dynamics of the processing center of the process! What is the fundamental reason
- 500 ° C ultra -strong aluminum alloy! This problem is overcome
- How much do you know about the hometown of machine tools and molds, how much do

 BACK
BACK MT HOME
MT HOME Navbar
Navbar